To gain insights into high functioning autism and emotions, it is essential to first understand the condition itself. High functioning autism is a term used to describe individuals on the autism spectrum who have average or above-average intellectual abilities and good verbal skills. These individuals may exhibit milder symptoms compared to those with severe autism.
Overview of High Functioning Autism
High functioning autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and restricted or repetitive behaviors. While every individual with high functioning autism is unique, there are common traits and patterns that are observed.
Individuals with high functioning autism may have difficulty understanding and expressing emotions, which can impact their emotional well-being and relationships. They may struggle with recognizing and interpreting nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, making it challenging for them to understand the emotions of others. This can sometimes lead to difficulties in emotional communication.
Characteristics of High Functioning Autism
Some common characteristics of high functioning autism include:
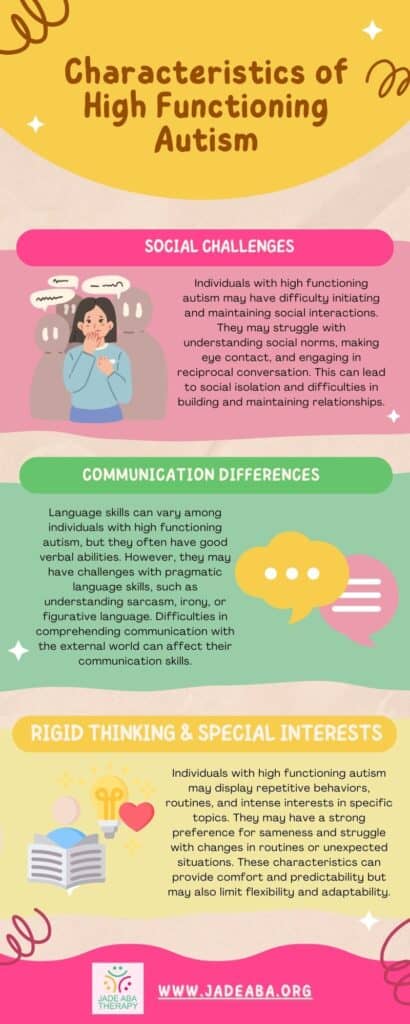
Understanding the overview and characteristics of high functioning autism is crucial in providing support and creating an environment that fosters emotional well-being for individuals on the autism spectrum. In the following sections, we will explore the emotional challenges faced by individuals with high functioning autism and discuss strategies to cope with and support their emotional well-being.
Emotional Challenges
Individuals with high functioning autism often face unique emotional challenges that can impact their daily lives and interactions with others. These challenges are rooted in difficulties with emotional communication and can have a significant impact on social interactions.
Difficulties with Emotional Communication
Emotional communication plays a crucial role in how individuals connect with others and navigate social situations. However, individuals on the autism spectrum often struggle with this aspect of communication. They may have challenges understanding and expressing their own emotional feelings, as well as comprehending the emotional cues conveyed by others. These difficulties in emotional communication can lead to misunderstandings and may contribute to social isolation.
Autistic individuals may find it challenging to interpret nonverbal cues related to emotions, such as facial expressions and body language. This can make it difficult for them to understand the emotions of others and respond appropriately. As a result, they may struggle to form and maintain relationships, as emotional communication is a fundamental aspect of building connections with others.
Impact on Social Interactions
The impact of emotional challenges in high functioning autism extends beyond communication difficulties. These challenges can affect the development of empathy and perspective-taking skills. Autistic individuals may find it challenging to express their own emotions effectively, which can make it difficult for others to understand their needs and experiences. Similarly, they may struggle to understand the emotions and perspectives of those around them.
The difficulties in emotional communication can create barriers to social interactions. Autistic individuals may face challenges in initiating and sustaining conversations, particularly when it comes to discussing emotions. They may also have trouble navigating social situations that require understanding and responding to the emotions of others. These difficulties can contribute to feelings of social anxiety and isolation.
By understanding the emotional challenges faced by individuals with high functioning autism, we can better support and empower them in their daily lives. Strategies for developing emotional awareness and regulation skills, creating safe and understanding environments, and encouraging open communication can all play a significant role in helping individuals on the autism spectrum navigate their emotions and improve their social interactions.

Coping Strategies
Individuals with high functioning autism often face challenges when it comes to understanding and managing their emotions. However, there are coping strategies that can help them develop emotional awareness and regulation skills, leading to improved emotional well-being.
Developing Emotional Awareness
Developing emotional awareness is an essential first step for individuals with high functioning autism. This involves recognizing and identifying different emotions, both in themselves and in others. By understanding their own emotions, individuals with autism can better navigate social interactions and communicate their needs effectively.
To develop emotional awareness, various strategies can be employed. These may include:
- Using visual aids: Visual supports, such as emotion cards or charts, can help individuals with autism recognize and label different emotions. These visual cues provide a concrete representation of emotions, making them easier to grasp.
- Role-playing: Engaging in role-playing activities allows individuals to practice recognizing and responding to different emotional cues. This can be done through scenarios or social stories that depict various emotions and appropriate responses.
- Encouraging self-reflection: Providing opportunities for individuals to reflect on their own emotions and experiences can enhance their emotional awareness. Journaling or engaging in discussions about feelings and emotions can be beneficial for this purpose.
Building Emotional Regulation Skills
Emotional regulation refers to the ability to manage and control emotions in a healthy and appropriate manner. Individuals with high functioning autism can face challenges in regulating their emotions, which can lead to difficulties in social interactions and overall well-being. However, there are strategies that can help build emotional regulation skills.
- Deep breathing exercises: Deep breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help individuals with autism calm themselves during moments of emotional distress. Encouraging slow, deep breaths can activate the body’s relaxation response and promote emotional regulation.
- Sensory strategies: Sensory input can play a crucial role in emotional regulation for individuals with autism. Providing sensory tools, such as stress balls or fidget toys, can help them redirect their attention and manage overwhelming emotions.
- Social stories and visual supports: Social stories, which provide step-by-step guidance on appropriate emotional responses, can assist individuals in understanding and regulating their emotions. Visual supports, such as emotion thermometers or coping strategy charts, can also aid in identifying and implementing effective emotional regulation techniques.
By developing emotional awareness and building emotional regulation skills, individuals with high functioning autism can better navigate their emotions and enhance their overall well-being.
Creating a Safe and Supportive Environment
Here are some strategies to create a safe and understanding environment for individuals with high functioning autism:
- Establish clear rules and expectations: Clearly communicate rules and expectations to provide structure and predictability.
- Maintain consistent routines: Consistency in daily routines can help individuals with autism feel more secure and reduce anxiety.
- Provide sensory accommodations: Sensory sensitivities are common among individuals with autism. Make adjustments to the environment, such as using noise-canceling headphones or providing a quiet space, to minimize sensory overload.
By implementing these strategies, caregivers can create an environment that supports emotional well-being and helps individuals with autism thrive.
Encouraging Open Communication
Open communication plays a crucial role in supporting individuals with high functioning autism. Allowing them to express their emotions and needs effectively fosters better understanding and connection with others..
Consider the following approaches to encourage open communication:
- Use visual supports: Visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules, can enhance communication and emotional expression[^4^]. These tools provide visual cues and help individuals with autism understand and navigate social situations.
- Practice active listening: Give individuals with autism your full attention and validate their emotions. Encourage them to express their thoughts and feelings, and demonstrate empathy towards their experiences.
- Promote self-advocacy: Encourage individuals with high functioning autism to advocate for themselves by teaching them self-advocacy skills. This empowers them to communicate their needs and preferences effectively.
By fostering open communication, caregivers can better understand the emotional experiences of individuals with autism and provide appropriate support.
Remember, each individual with high functioning autism is unique, so it’s important to tailor the supportive strategies to their specific needs and preferences. Providing opportunities for individuals with autism to engage in activities they enjoy and excel at can also boost their self-esteem and overall emotional well-being.

Seeking Professional Help
For individuals with high functioning autism, seeking professional help is an important step in addressing emotional challenges and promoting overall well-being. Therapy options and early intervention play crucial roles in supporting individuals on the autism spectrum. Let’s explore the available therapy options and the importance of early intervention.
Therapy Options
Therapy can provide valuable support and guidance for individuals with high functioning autism. Several therapy options have shown positive outcomes in improving emotional communication skills and overall emotional well-being. These therapy options include:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapy approach that focuses on identifying and changing patterns of thinking and behavior. It can help individuals with high functioning autism develop coping strategies, manage emotions, and improve social interactions.
Social Skills Training: Social skills training aims to enhance social interaction and communication skills. This type of therapy can be beneficial for individuals with high functioning autism by providing them with the tools and techniques to navigate social situations effectively.
Speech Therapy: Speech therapy focuses on improving communication skills, including expressive and receptive language abilities. It can help individuals with high functioning autism develop better emotional communication skills, such as understanding and expressing emotions effectively.
It’s important to note that therapy options may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and strengths. Consulting with a qualified professional can help determine the most suitable therapy approach for each person.
Importance of Early Intervention
Research consistently emphasizes the importance of early intervention for individuals with high functioning autism. Early intervention refers to the identification and support provided to individuals at a young age, typically before the age of three. Early intervention programs target specific areas of development and aim to address challenges effectively.
Studies have shown that early intervention programs focusing on emotional regulation skills have significant positive outcomes for individuals with high functioning autism Early intervention allows for targeted therapy and support to address emotional challenges effectively.
By starting intervention early, individuals with high functioning autism can receive appropriate support and guidance during critical periods of development. This can lead to improved emotional regulation, social interactions, and emotional communication skills.
Early intervention programs often involve a combination of individual therapy and family therapy. Family therapy can support emotional communication development and create a supportive environment for the individual.
In conclusion, seeking professional help through therapy options and early intervention can provide valuable support for individuals with high functioning autism. These interventions offer strategies and techniques to address emotional challenges, improve emotional communication skills, and enhance overall well-being. By utilizing these resources, individuals with high functioning autism can navigate their emotions and develop the necessary skills for successful social interactions.
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7375152/
- https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2012-14101-001https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/aspergers-syndrome-emotional-intelligence-1002124
- https://medium.com/@theaspieworld/aspergers-and-emotions-this-is-why-autistic-people-have-issues-with-emotion-f1cad90bdfb2